PHYSICAL THERAPY
01
Back Pain

What is lower back pain?
While lower back pain is incredibly common among adults, exact symptoms and causes vary widely from patient to patient. Some patients may experience dull, aching pain that develops and worsens gradually over time, while others may experience sharp and sudden pain.
Common Types of Lower Back Pain Includes
- Joint irritation
- Disk injuries
- Sciatica or Pinched Nerves
- Posture imbalance
- Muscle spasms and strains
- Arthritis
Low back pain is usually a result of muscle strain, which can occur when a patient lifts heavy items, bends or twists into awkward positions, or sits or stands for too long, although there are a number of other potential causes.
Many patients find that their lower back pain can be resolved with at-home treatments such as icing and rest, but if the pain is severe and persistent or interferes with day-to-day activities, it’s recommended that patients seek medical attention.
Lower Back Pain Physical Therapy Treatments
01 Passive Physical Therapy
Also known as modalities, it involves things being done to the patient. It involves hot treatment, using a heating pad, to warm the injured area prior to exercising and cold treatment, using an ice pack, to cool the same area after exercising to soothe muscle tissue.
02 Active Physical Therapy
This form of treatment focuses on unique and specific stretching exercises. Physical therapist in Fort Lauderdale, FL mainly recommend this course of treatment to most patients suffering from lower back pains.
Lower back pain is commonly caused by trauma to the lumbar spine, lifting heavy items, poor sitting posture and frequently bending forward.
Physical therapy enables you to regain back range-mobility and strength making movement easy.
02
Neck Pain
Physical Therapy Can Help Relieve Those Pains in Your Neck!
When someone experiences neck pain, it typically runs from the base of their skull to the top of their shoulder blades, finally settling in the back of the neck. There are a number of reasons why neck pain may occur. The pain can vary in severity, from a constant dull ache to sharp and stabbing pains. Neck pain can sometimes include additional symptoms, including but not limited to:
- Loss of sleep due to pain and discomfort.
- Numbness or tingling into the upper extremities.
- Headaches.
- Arm weakness.
- Inability to fully stand up or sit up straight.
- Stiffness and muscle tightness in the upper body.
- Discomfort and pain when remaining in the same position for too long.
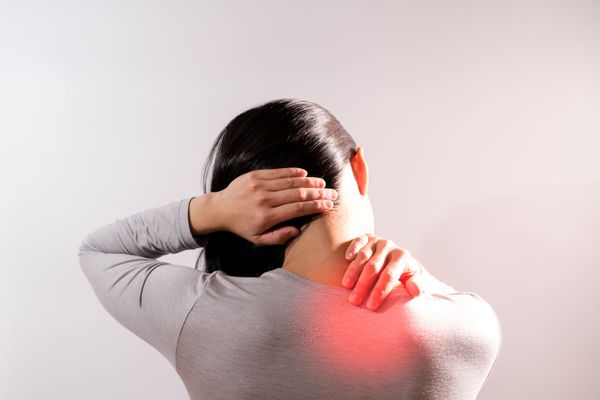
What’s Causing My Neck Pain?
Neck pain is most commonly caused by an injury to the tissues or bone structures in the neck; however, certain degenerative conditions can also lead to neck pain.
Some common conditions that give you a pain in your neck include:
01 Illnesses
Certain diseases and ailments can result in neck pain, such as rheumatoid arthritis, meningitis, or cancer.
02 Nerve Compression
If you have a herniated disc in your neck, or narrowing of the foramen (space where the nerves exit the spine), the nerves that branch out from your spinal cord can become compressed. In some cases, nerve pain can even extend from the neck all the way down to the hands and fingers — a condition known as “radiculopathy.”
03 Joint Degeneration
Much like any other joint in your body, the neck joints can erode with age, causing pain. Conditions such as osteoarthritis can also reduce the cartilage between the vertebrae in the neck, also resulting in neck pain.
04 Injuries
Whiplash is one of the most common injuries that results in neck pain, typically sustained by an automobile or high-impact sports collision. This is known as a “strain” injury, causing the head to whip rapidly back-and-forth, thus affecting the soft tissues in the back of the neck.
05 Muscle Strains
The muscles in your neck can become strained by overuse. Even something as simple as sitting at your desk all day with your neck craned toward the computer screen can lead to a strain in your neck muscles.
03
Knee Pain
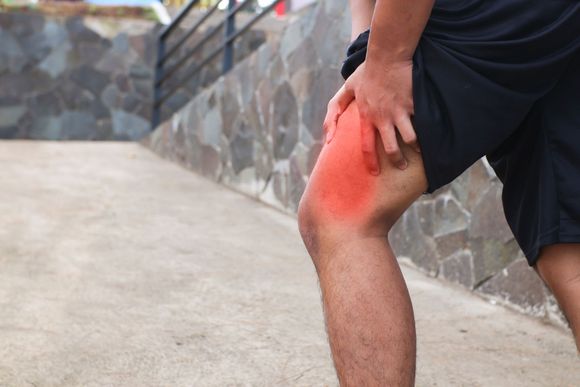
What Causes Knee Pain?
Sports injuries represent the top cause of knee pain. Most of these injuries occur when you twist the joint or take a direct hit to the knee. In many cases, the resulting injury affects the ligaments and meniscus (the cartilage between the two leg bones in the joint).
Many people develop overuse injuries because their knees sustain significant daily wear and tear. As you get older, chances are your knee pain is due to arthritis.
Dr. Orlando frequently treats knee pain caused by:
- Osteoarthritis
- Torn ACL (anterior cruciate ligament)
- Torn meniscus
- Tendonitis
- Bursitis
- Joint dislocation
- Runner’s knee
What Other Symptoms Accompany Knee Pain?
You could have knee pain without other symptoms, but chances are the condition responsible for your pain will cause one or more of the following:
- Inflammation
- Swelling
- Limited joint movement
- Bruising
- Clicking or popping
- Locked knee joint
- Inability to bear weight on your knee
If you tear a ligament, the joint may become unstable, making it feel like your knee could give out.
How is Knee Pain Treated?
Dr. Walters carefully evaluates your knee and creates a treatment plan that’s best for the cause and severity of your pain.
Your initial treatment may include ice, heat, rest, anti-inflammatory medications, and possibly bracing to stabilize or immobilize the joint. As soon as possible, you start physical therapy to restore joint movement and strength.
If your pain doesn’t improve or you have a slow-healing injury, Dr. Walters recommends additional treatments, such as:
01 Joint Injections
Ultrasound-guided knee injections typically deliver steroids to reduce inflammation. Patients with osteoarthritis may receive an injection containing hyaluronic acid, which lubricates the joint and improves movement.
02 Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injections speeds up the healing process, reduces inflammation, and draws regenerative stem cells to the area.
04
Hip Pain
You might be roaming about to have a solution for your hip pain, perhaps a bit tense. Dr. Walters has the appropiate therapy solution to this pain. Hip pain is a common issue with thousands of people from all walks of life. We put huge stress on the hip in many ways and at a stage, it begins to backfire. Or there might be an unexpected injury. Then we cannot but think of a therapeutic approach. And luckily physical therapies are exercise-based, enjoyable. You just need to choose the right therapy hub to overcome this pain.
Hips And its Functions
In anatomy, the hip is the joint between the thighbone and the pelvis and the area adjacent to it. This joint is all about a ball-and-socket. A lining tissue named Synovium surrounds the hip joint and produces necessary fluid. The thigh bone or femur and the pelvis are two vital bones. And the round head of our thighbone facilitates the limb rotates freely. It connects the leg to the trunk of the body.

Common Causes of Hip Pain
We want our patients to be knowledgeable. It will help them narrate their problem histories properly. So here we present the most common causes of hip pain.
These are:
- Hip fractures
- Osteonecrosis
- Iliotibial band syndrome
- Arthritis
- Septic arthritis
- Muscle train
- Hematoma
- Bursitis
- Tendinitis
- Cancer
- Sciatica
- Gaucher’s disease
- Hip labral tear
When to Take Action
There are certain conditions when you must take your hip pain seriously and act thereby. Whenever you see you are unable to move your leg or hip, or you feel the hip joint displaced, or there is extreme pain you must meet a doctor immediately. Also, there might be infectious symptoms like chills or redness. Sometimes you may fail to bear a heavy thing. Generally, in such cases, doctors do recommend physical therapy after their treatment.
Physical Therapy for Hip Pain
Our physical therapists can treat the following causes of hip pain and discomfort:
- Sciatica pain
- Hip Arthritis
- Trochanteric Bursitis
- Anterior hip pain
- Lateral hip pain
Based on the possible causes our certified physical therapists will suggest you the best treatments for hip pain. If you are suffering from hip pain, contact us today.
05
Shoulder Pain

Regarding the Shoulder And Its Pain
The shoulder is the summation of several joints that give us strength and range of motion to the arm. In other words, it is a combination of the collarbone, upper-arm bone, and shoulder blade. On the other hand, shoulder pain or impingement is a problem with the rotator cuff. The most possible causes of this pain are:
- Loss of cartilage
- Irregular posture
- Heart attack
- Tension in the muscles between the neck & shoulder
- Dislocation of the shoulder
- Spinal cord coup
- Burning in the ‘bursa’
- Frozen of tissues
- Damage to the muscle and tendons
- Bone spurs
- Arthritis
Who doesn’t know that having a sound body is the precondition of having a sound mind! Sometimes we do shroud or ignore our shoulder pain and repent afterward. Harboring pain is simply absurd. It’s all about forfeiting in near future. Hopefully, you don’t want to go astray.
How Will Physical Therapy Help My Shoulder Pain?
Physical therapy is a natural, easy, and comfortable way to find relief for shoulder pain, without the need for harmful drugs or invasive surgery. I have treated a number of conditions resulting in shoulder pain, with patients finding improvement and relief after just a few short sessions – and sometimes less!
Once we have established the cause of your shoulder pain, we can create a specialized combination of physical therapy methods to manage and relieve your pain. Gentle manual therapy helps to restore normal joint movement, ease soft tissue restrictions, and promote circulation, while specific therapeutic exercises restore strength, and the correct sequence of muscle activation around the shoulder joint. Finally, we teach you techniques to enhance your strength and to prevent the recurrence of future shoulder problems.

